Scabies (‘the itch’) is a contagious skin disease. Read more about the condition and the symptoms of scabies here.
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite (itch mite). This is a small insect that you cannot see with the naked eye. The mite digs tunnels into the surface of your skin and lays eggs there. Your skin then has an allergic reaction to the mite, which causes itching. Read more about the itch mite.
Crusted scabies: a more severe form of scabies
In addition to ‘regular’ scabies, some people, like those in poor health, can get a more severe form of scabies. They carry a large amount of mites and are highly contagious. This form of scabies is called crusted or Norwegian scabies. It must be treated with more measures than regular scabies. A dermatologist must confirm this diagnosis. You can find more information in the crusted scabies fact sheet (in Dutch).
What are the symptoms of scabies?
You can recognise scabies by the following symptoms:
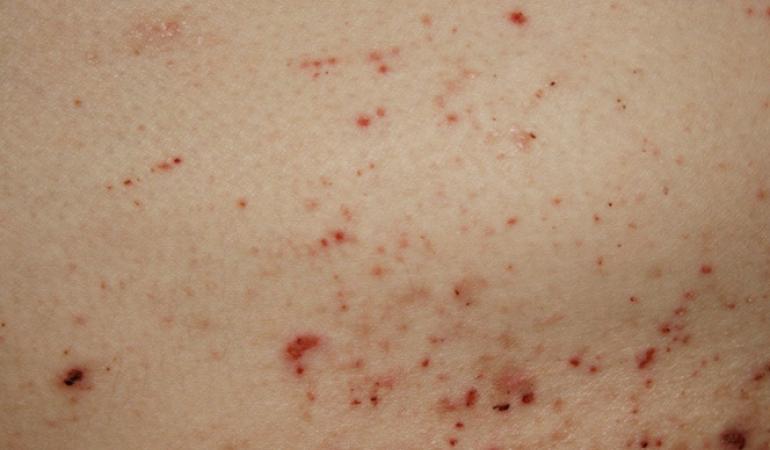
- Itching that continues to get worse. You can have itching all over your body, especially at night and when it is hot. The itching is an allergic reaction to the mites, their eggs and their faeces.
- Blisters, red lumps or flaky skin on your palms, between your fingers, on your wrists, elbows, feet and genitals.
- You may also see red stripes on your skin. This is where the mites have dug tunnels.
- Children up to the age of four can also have itching and blisters on their head.
If this is the first time you have had scabies, the time between getting it and feeling symptoms is two to six weeks. If you have had scabies before, you will start itching after a few days.
Image: close-up of skin with scabies
Confirming if you have scabies
If you want to know for sure if you have scabies, you need to see a general practitioner or dermatologist. The doctor will examine flakes of your skin under a microscope to check for mites and eggs. Sometimes the doctor will use a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test to check whether there are mites in the flakes of skin.
Scabies does not go away on its own. That is why it is important that you get treatment. This also stops the symptoms from getting worse and stops you from spreading scabies to others. Your body does not build up immunity to scabies, so you can get scabies more than once.
Scabies is more common in the winter than in the summer.
Can I go to work or school if I have scabies?
You can go to work or school as usual. If you have intensive skin-to-skin contact with other people at work or school regularly or for a long time, do not go to work or school until 12 hours after treatment. Always talk about this with your line manager, company doctor or mentor.
The itch mite
The itch mite looks like a tiny spider. It has a white, oval-shaped body and eight legs. The mite has bristles and spines on its back that help it burrow into the skin. The itch mite is smaller than 0.5 mm, so you can only see it under a microscope.
An itch mite can live in the skin for four to six weeks. Outside the human body, most mites die within three days. However, mites can survive longer at temperatures below room temperature (18 °C).